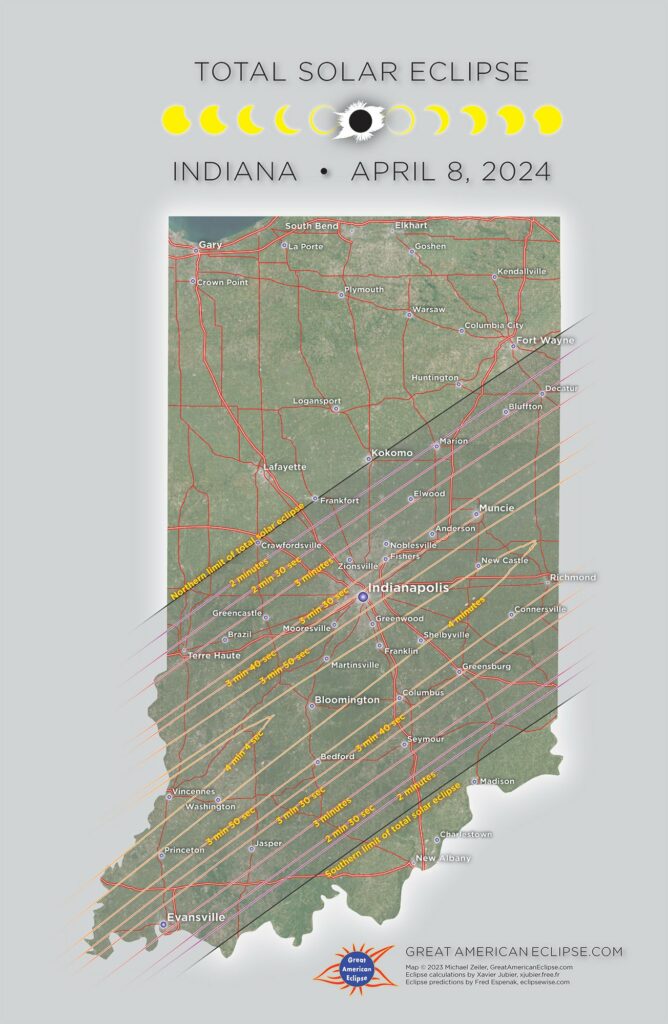
It’s a common question, and the answer lies in the fact that the Moon’s orbit around Earth is slightly tilted compared to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. This means that most of the time when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, it doesn’t completely block out our view of the Sun.
A lunar eclipse occurs when Earth is directly between the Sun and Moon, blocking sunlight from reaching the Moon. Similarly, a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between Earth and the Sun. Both of these events are rare because they require perfect alignment of all three celestial bodies.
The tilt of our orbits also affects how often we experience eclipses. Since both eclipses occur during a full moon, they can only happen once every 29 days when there is a full moon. However, since Earth’s orbit is tilted by about 5 degrees relative to that of the Moon, these eclipses don’t always occur at exactly the same time each month.
In addition to this orbital tilt, there are other factors that affect how often we experience lunar or solar eclipses. For example, if an eclipse happens near one of its nodes (the points where its orbit crosses Earth’s orbital plane), then it will be more likely to be visible from certain parts of Earth than others. This means that some areas may experience more frequent eclipses than others due to their location on our planet!
So while it may seem like lunar and solar eclipses should happen every month, in reality, they are quite rare due to several factors including orbital tilt and location on our planet.